舌肌功能训练联合心理疏导对错畸形早期矫治患儿自我效能感的影响
赫 佳
大连市口腔医院儿童口腔科,辽宁大连 116021
[摘要]目的 探讨舌肌功能训练联合心理疏导对错 畸形早期矫治患儿的临床效果及自我效能感的影响。方法 选取2018年8月~2019年12月于大连市口腔医院儿童口腔科收治的136例错
畸形早期矫治患儿的临床效果及自我效能感的影响。方法 选取2018年8月~2019年12月于大连市口腔医院儿童口腔科收治的136例错 畸形患儿作为研究对象。按照随机数字表分为观察组(68例)与对照组(68例)。两组早期矫治时均进行心理疏导,观察组在此基础上给予舌肌功能训练,干预周期为8周。评估两组矫正效果,并记录治疗前后前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度、下前牙唇倾度、自我效能感变化及护理满意度。结果 观察组总有效率高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预前,两组前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度及下前牙唇倾度比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后,两组前牙覆盖及上切牙唇倾度均低于干预前,下前牙唇倾度均高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后,观察组前牙覆盖及上切牙唇倾度均低于对照组,下前牙唇倾度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预前,两组自我效能感评分的比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后,两组自我效能感评分高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后,观察组自我效能感评分高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组护理总满意度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 舌肌功能训练应用于错
畸形患儿作为研究对象。按照随机数字表分为观察组(68例)与对照组(68例)。两组早期矫治时均进行心理疏导,观察组在此基础上给予舌肌功能训练,干预周期为8周。评估两组矫正效果,并记录治疗前后前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度、下前牙唇倾度、自我效能感变化及护理满意度。结果 观察组总有效率高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预前,两组前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度及下前牙唇倾度比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后,两组前牙覆盖及上切牙唇倾度均低于干预前,下前牙唇倾度均高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后,观察组前牙覆盖及上切牙唇倾度均低于对照组,下前牙唇倾度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预前,两组自我效能感评分的比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后,两组自我效能感评分高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后,观察组自我效能感评分高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组护理总满意度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 舌肌功能训练应用于错 畸形早期矫治患儿的心理护理中,效果良好,能改善前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度及下前牙唇倾度,提高患儿自我效能感,同时还能促进护患关系和谐发展。
畸形早期矫治患儿的心理护理中,效果良好,能改善前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度及下前牙唇倾度,提高患儿自我效能感,同时还能促进护患关系和谐发展。
 畸形早期矫治患儿的临床效果及自我效能感的影响。方法 选取2018年8月~2019年12月于大连市口腔医院儿童口腔科收治的136例错
畸形早期矫治患儿的临床效果及自我效能感的影响。方法 选取2018年8月~2019年12月于大连市口腔医院儿童口腔科收治的136例错 畸形患儿作为研究对象。按照随机数字表分为观察组(68例)与对照组(68例)。两组早期矫治时均进行心理疏导,观察组在此基础上给予舌肌功能训练,干预周期为8周。评估两组矫正效果,并记录治疗前后前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度、下前牙唇倾度、自我效能感变化及护理满意度。结果 观察组总有效率高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预前,两组前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度及下前牙唇倾度比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后,两组前牙覆盖及上切牙唇倾度均低于干预前,下前牙唇倾度均高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后,观察组前牙覆盖及上切牙唇倾度均低于对照组,下前牙唇倾度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预前,两组自我效能感评分的比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后,两组自我效能感评分高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后,观察组自我效能感评分高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组护理总满意度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 舌肌功能训练应用于错
畸形患儿作为研究对象。按照随机数字表分为观察组(68例)与对照组(68例)。两组早期矫治时均进行心理疏导,观察组在此基础上给予舌肌功能训练,干预周期为8周。评估两组矫正效果,并记录治疗前后前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度、下前牙唇倾度、自我效能感变化及护理满意度。结果 观察组总有效率高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预前,两组前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度及下前牙唇倾度比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后,两组前牙覆盖及上切牙唇倾度均低于干预前,下前牙唇倾度均高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后,观察组前牙覆盖及上切牙唇倾度均低于对照组,下前牙唇倾度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预前,两组自我效能感评分的比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后,两组自我效能感评分高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后,观察组自我效能感评分高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组护理总满意度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 舌肌功能训练应用于错 畸形早期矫治患儿的心理护理中,效果良好,能改善前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度及下前牙唇倾度,提高患儿自我效能感,同时还能促进护患关系和谐发展。
畸形早期矫治患儿的心理护理中,效果良好,能改善前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度及下前牙唇倾度,提高患儿自我效能感,同时还能促进护患关系和谐发展。[关键词]舌肌功能训练;心理疏导;错 畸形;早期矫治;自我效能感
畸形;早期矫治;自我效能感
 畸形;早期矫治;自我效能感
畸形;早期矫治;自我效能感错 畸形通常是指人体牙颌与颅面间位置不调而引起的畸形,部分医学专家认为与家族遗传、替牙畸形、生活因素等息息相关,其临床症状多表现为牙齿错位、排列拥挤不整齐、
畸形通常是指人体牙颌与颅面间位置不调而引起的畸形,部分医学专家认为与家族遗传、替牙畸形、生活因素等息息相关,其临床症状多表现为牙齿错位、排列拥挤不整齐、 关系错乱等,能引起龋齿、牙周炎等并发症,严重者可直接影响牙颌发育,导致患儿咀嚼功能低下,引起胃肠功能异常,还可影响美观,在一定程度上使得患儿心理及精神出现障碍[1-2]。及时早期矫治是主要治疗方针,如矫正牙套,能解除排列拥挤及切牙倾斜度,减小切牙覆颌及前牙覆盖,但其治疗时间较长,可能会影响牙口美观,造成一定心理负担,治疗效果并不理想,因此会配合心理干预来消除患儿负性情绪,增强治疗信心[3-4]。宋艳[5]提出护理干预配合舌肌功能训练应用于错
关系错乱等,能引起龋齿、牙周炎等并发症,严重者可直接影响牙颌发育,导致患儿咀嚼功能低下,引起胃肠功能异常,还可影响美观,在一定程度上使得患儿心理及精神出现障碍[1-2]。及时早期矫治是主要治疗方针,如矫正牙套,能解除排列拥挤及切牙倾斜度,减小切牙覆颌及前牙覆盖,但其治疗时间较长,可能会影响牙口美观,造成一定心理负担,治疗效果并不理想,因此会配合心理干预来消除患儿负性情绪,增强治疗信心[3-4]。宋艳[5]提出护理干预配合舌肌功能训练应用于错 畸形患儿的早期矫正,可有效改善牙周健康,提高矫正效果,增强咬合。本研究将大连市口腔医院136例错
畸形患儿的早期矫正,可有效改善牙周健康,提高矫正效果,增强咬合。本研究将大连市口腔医院136例错 畸形患儿作为观察对象,进一步分析舌肌功能训练运用于早期矫治的临床应用,现报道如下。
畸形患儿作为观察对象,进一步分析舌肌功能训练运用于早期矫治的临床应用,现报道如下。
 畸形通常是指人体牙颌与颅面间位置不调而引起的畸形,部分医学专家认为与家族遗传、替牙畸形、生活因素等息息相关,其临床症状多表现为牙齿错位、排列拥挤不整齐、
畸形通常是指人体牙颌与颅面间位置不调而引起的畸形,部分医学专家认为与家族遗传、替牙畸形、生活因素等息息相关,其临床症状多表现为牙齿错位、排列拥挤不整齐、 关系错乱等,能引起龋齿、牙周炎等并发症,严重者可直接影响牙颌发育,导致患儿咀嚼功能低下,引起胃肠功能异常,还可影响美观,在一定程度上使得患儿心理及精神出现障碍[1-2]。及时早期矫治是主要治疗方针,如矫正牙套,能解除排列拥挤及切牙倾斜度,减小切牙覆颌及前牙覆盖,但其治疗时间较长,可能会影响牙口美观,造成一定心理负担,治疗效果并不理想,因此会配合心理干预来消除患儿负性情绪,增强治疗信心[3-4]。宋艳[5]提出护理干预配合舌肌功能训练应用于错
关系错乱等,能引起龋齿、牙周炎等并发症,严重者可直接影响牙颌发育,导致患儿咀嚼功能低下,引起胃肠功能异常,还可影响美观,在一定程度上使得患儿心理及精神出现障碍[1-2]。及时早期矫治是主要治疗方针,如矫正牙套,能解除排列拥挤及切牙倾斜度,减小切牙覆颌及前牙覆盖,但其治疗时间较长,可能会影响牙口美观,造成一定心理负担,治疗效果并不理想,因此会配合心理干预来消除患儿负性情绪,增强治疗信心[3-4]。宋艳[5]提出护理干预配合舌肌功能训练应用于错 畸形患儿的早期矫正,可有效改善牙周健康,提高矫正效果,增强咬合。本研究将大连市口腔医院136例错
畸形患儿的早期矫正,可有效改善牙周健康,提高矫正效果,增强咬合。本研究将大连市口腔医院136例错 畸形患儿作为观察对象,进一步分析舌肌功能训练运用于早期矫治的临床应用,现报道如下。
畸形患儿作为观察对象,进一步分析舌肌功能训练运用于早期矫治的临床应用,现报道如下。1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2018年8月至2019年12月于大连市口腔医院儿童口腔科收治的136例错 畸形患儿作为研究对象。按照随机数字表分为观察组(68例)与对照组(68例)。对照组中,男35例,女33例;年龄5~10岁,平均(7.48±2.25)岁;体重指数(BMI)20~25 kg/m2,平均(22.46±1.87)kg/m2;中性错颌25例,远中错颌24例,近中错颌19例。观察组中,男36例,女32例;年龄5~10岁,平均(7.56±2.37)岁;BMI 21~25 kg/m2,平均(22.84±1.68)kg/m2;中性错颌25例,远中错颌24例,近中错颌19例。两组患儿的性别、年龄、BMI、疾病类型等一般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。纳入标准:①所有患儿均经X线测量确诊为错
畸形患儿作为研究对象。按照随机数字表分为观察组(68例)与对照组(68例)。对照组中,男35例,女33例;年龄5~10岁,平均(7.48±2.25)岁;体重指数(BMI)20~25 kg/m2,平均(22.46±1.87)kg/m2;中性错颌25例,远中错颌24例,近中错颌19例。观察组中,男36例,女32例;年龄5~10岁,平均(7.56±2.37)岁;BMI 21~25 kg/m2,平均(22.84±1.68)kg/m2;中性错颌25例,远中错颌24例,近中错颌19例。两组患儿的性别、年龄、BMI、疾病类型等一般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。纳入标准:①所有患儿均经X线测量确诊为错 畸形[6],且均为首次参与早期矫治;②患儿口腔卫生良好,牙体完整,且各项生命体征正常;③患儿及其家属均自愿参加本次研究并签署知情同意书;④家属无精神及沟通意识障碍。排除标准:①伴有牙齿缺失、龋齿等口腔疾病者;②严重牙齿畸形者;③无法全程接受治疗者;④合并严重心、肺、肝等功能障碍者。本研究经大连市口腔医院医学伦理委员会审核批准。
畸形[6],且均为首次参与早期矫治;②患儿口腔卫生良好,牙体完整,且各项生命体征正常;③患儿及其家属均自愿参加本次研究并签署知情同意书;④家属无精神及沟通意识障碍。排除标准:①伴有牙齿缺失、龋齿等口腔疾病者;②严重牙齿畸形者;③无法全程接受治疗者;④合并严重心、肺、肝等功能障碍者。本研究经大连市口腔医院医学伦理委员会审核批准。
 畸形患儿作为研究对象。按照随机数字表分为观察组(68例)与对照组(68例)。对照组中,男35例,女33例;年龄5~10岁,平均(7.48±2.25)岁;体重指数(BMI)20~25 kg/m2,平均(22.46±1.87)kg/m2;中性错颌25例,远中错颌24例,近中错颌19例。观察组中,男36例,女32例;年龄5~10岁,平均(7.56±2.37)岁;BMI 21~25 kg/m2,平均(22.84±1.68)kg/m2;中性错颌25例,远中错颌24例,近中错颌19例。两组患儿的性别、年龄、BMI、疾病类型等一般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。纳入标准:①所有患儿均经X线测量确诊为错
畸形患儿作为研究对象。按照随机数字表分为观察组(68例)与对照组(68例)。对照组中,男35例,女33例;年龄5~10岁,平均(7.48±2.25)岁;体重指数(BMI)20~25 kg/m2,平均(22.46±1.87)kg/m2;中性错颌25例,远中错颌24例,近中错颌19例。观察组中,男36例,女32例;年龄5~10岁,平均(7.56±2.37)岁;BMI 21~25 kg/m2,平均(22.84±1.68)kg/m2;中性错颌25例,远中错颌24例,近中错颌19例。两组患儿的性别、年龄、BMI、疾病类型等一般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。纳入标准:①所有患儿均经X线测量确诊为错 畸形[6],且均为首次参与早期矫治;②患儿口腔卫生良好,牙体完整,且各项生命体征正常;③患儿及其家属均自愿参加本次研究并签署知情同意书;④家属无精神及沟通意识障碍。排除标准:①伴有牙齿缺失、龋齿等口腔疾病者;②严重牙齿畸形者;③无法全程接受治疗者;④合并严重心、肺、肝等功能障碍者。本研究经大连市口腔医院医学伦理委员会审核批准。
畸形[6],且均为首次参与早期矫治;②患儿口腔卫生良好,牙体完整,且各项生命体征正常;③患儿及其家属均自愿参加本次研究并签署知情同意书;④家属无精神及沟通意识障碍。排除标准:①伴有牙齿缺失、龋齿等口腔疾病者;②严重牙齿畸形者;③无法全程接受治疗者;④合并严重心、肺、肝等功能障碍者。本研究经大连市口腔医院医学伦理委员会审核批准。1.2 方法
两组患儿早期矫治时均进行心理疏导,干预周期为8周,具体如下:①医护人员首先要具备全面的口腔医学知识,以便在护理过程中及时解决相应的问题,定期考核知识水平与技能操作,以提高护理效果。②患儿治疗期间,医护人员组织成立护理小组,通过图片、视频、幻灯片等娱乐方式进行错 畸形的相关知识宣教,详细告知家属疾病原因、治疗方法、矫正必要性、并发症、预后效果等,由家属带领患儿进行相关护理操作,以提高家属疾病认知度,从而提高患儿治疗依从性。③根据不同患儿的心理状态,医护人员与家属要耐心解答患儿问题,解答各种疑难,坚定治疗信心;对于病情较为严重或矫正效果不佳的患儿,医护人员与家属应给予安慰鼓励,使患儿感受到温暖与关爱,增加其信赖度。④要求定期复查,医护人员可通过微信、电话等形式延续护理指导,教会家属如何应对各种问题,并督促患儿保持良好的生活习惯,若遇到牙龈红肿、牙齿松动等现象,及时就医进行相关治疗,以防病情加重,影响恢复。
畸形的相关知识宣教,详细告知家属疾病原因、治疗方法、矫正必要性、并发症、预后效果等,由家属带领患儿进行相关护理操作,以提高家属疾病认知度,从而提高患儿治疗依从性。③根据不同患儿的心理状态,医护人员与家属要耐心解答患儿问题,解答各种疑难,坚定治疗信心;对于病情较为严重或矫正效果不佳的患儿,医护人员与家属应给予安慰鼓励,使患儿感受到温暖与关爱,增加其信赖度。④要求定期复查,医护人员可通过微信、电话等形式延续护理指导,教会家属如何应对各种问题,并督促患儿保持良好的生活习惯,若遇到牙龈红肿、牙齿松动等现象,及时就医进行相关治疗,以防病情加重,影响恢复。
 畸形的相关知识宣教,详细告知家属疾病原因、治疗方法、矫正必要性、并发症、预后效果等,由家属带领患儿进行相关护理操作,以提高家属疾病认知度,从而提高患儿治疗依从性。③根据不同患儿的心理状态,医护人员与家属要耐心解答患儿问题,解答各种疑难,坚定治疗信心;对于病情较为严重或矫正效果不佳的患儿,医护人员与家属应给予安慰鼓励,使患儿感受到温暖与关爱,增加其信赖度。④要求定期复查,医护人员可通过微信、电话等形式延续护理指导,教会家属如何应对各种问题,并督促患儿保持良好的生活习惯,若遇到牙龈红肿、牙齿松动等现象,及时就医进行相关治疗,以防病情加重,影响恢复。
畸形的相关知识宣教,详细告知家属疾病原因、治疗方法、矫正必要性、并发症、预后效果等,由家属带领患儿进行相关护理操作,以提高家属疾病认知度,从而提高患儿治疗依从性。③根据不同患儿的心理状态,医护人员与家属要耐心解答患儿问题,解答各种疑难,坚定治疗信心;对于病情较为严重或矫正效果不佳的患儿,医护人员与家属应给予安慰鼓励,使患儿感受到温暖与关爱,增加其信赖度。④要求定期复查,医护人员可通过微信、电话等形式延续护理指导,教会家属如何应对各种问题,并督促患儿保持良好的生活习惯,若遇到牙龈红肿、牙齿松动等现象,及时就医进行相关治疗,以防病情加重,影响恢复。观察组在此基础上给予舌肌功能训练,首先确定舌尖位置,然后由专业医护人员及家属指导并协助患儿完成弹舌、绕舌、外伸、鼓腮等舌肌训练,每日30 min 左右,4~6次/d,其具体操作如下:①弹舌训练。患儿将舌尖舔在切牙乳头上,使得整个舌体贴在腭顶部,然后放松发生弹响声音,循环重复30下,2次/d,可有效强化舌部肌肉。②吸上腭训练。患儿舌尖舔在切牙乳头,采用吮吸的方式使整个舌体贴紧上腭,保持动作稳定2 min,2次/d。③舌外伸训练。患儿将尽可能张大嘴巴,在不碰到下切牙的前提下,把舌头往外伸,重复20下,增加舌肌力量。④瘦舌训练。将尽可能张大嘴巴,将舌头伸出并举起,然后缩回,每2 秒做1次动作交替,每次2 min,2次/d 强化舌肌上抬肌力。⑤唇肌训练。患儿抿嘴闭唇,使上下嘴唇尽量伸展,每次30 s,或者在唇间放一吸管,咬住吸管,维持30 s以上;也可采取爆破音训练,患儿将唇抿紧,尽量用力做吹气动作,必要时配合鼻呼吸,纠正口呼吸习惯。⑥鼓腮训练。患儿吸足一口气,尽量鼓起两腮,将嘴唇用食指按压住,脸部有明显酸胀感后,坚持动作5 s,然后缓慢喷出气体。
1.3 观察指标及评价标准
①评估两组矫正效果,其评定标准[7]包括显效:矫正后,牙齿排列整齐,前牙覆盖正常, 关系、面型显著改善且基本恢复正常;有效:矫正后,牙齿排列较整齐,前牙覆盖、
关系、面型显著改善且基本恢复正常;有效:矫正后,牙齿排列较整齐,前牙覆盖、 关系及面型均明显改善;无效:矫正后,牙齿排列无明显变化,前牙覆盖、
关系及面型均明显改善;无效:矫正后,牙齿排列无明显变化,前牙覆盖、 关系、面型无改善,总有效率=(显效+有效)例数/总例数×100%。②分别于干预前后,采用锥形束CT(CBCT)图像[8]测量并记录两组前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度及下前牙唇倾度。③分别于干预前后记录两组自我效能感评分,采用一般自我效能感量表(GSES)[9]进行评估,共10个项目,包括解决问题能力、心理状态、社会能力等,分为完全不正确、有点正确、多数正确及完全正确,分数越高说明自我效能感越强。④随访后记录两组护理满意度,根据文献[10]对患儿及其家属从护理评价、矫正效果、医护人员的专业性、随访工作等方面进行评估,分为满意、部分满意、不满意三个级别,总满意度=(满意+部分满意)例数/总例数×100%。
关系、面型无改善,总有效率=(显效+有效)例数/总例数×100%。②分别于干预前后,采用锥形束CT(CBCT)图像[8]测量并记录两组前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度及下前牙唇倾度。③分别于干预前后记录两组自我效能感评分,采用一般自我效能感量表(GSES)[9]进行评估,共10个项目,包括解决问题能力、心理状态、社会能力等,分为完全不正确、有点正确、多数正确及完全正确,分数越高说明自我效能感越强。④随访后记录两组护理满意度,根据文献[10]对患儿及其家属从护理评价、矫正效果、医护人员的专业性、随访工作等方面进行评估,分为满意、部分满意、不满意三个级别,总满意度=(满意+部分满意)例数/总例数×100%。
 关系、面型显著改善且基本恢复正常;有效:矫正后,牙齿排列较整齐,前牙覆盖、
关系、面型显著改善且基本恢复正常;有效:矫正后,牙齿排列较整齐,前牙覆盖、 关系及面型均明显改善;无效:矫正后,牙齿排列无明显变化,前牙覆盖、
关系及面型均明显改善;无效:矫正后,牙齿排列无明显变化,前牙覆盖、 关系、面型无改善,总有效率=(显效+有效)例数/总例数×100%。②分别于干预前后,采用锥形束CT(CBCT)图像[8]测量并记录两组前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度及下前牙唇倾度。③分别于干预前后记录两组自我效能感评分,采用一般自我效能感量表(GSES)[9]进行评估,共10个项目,包括解决问题能力、心理状态、社会能力等,分为完全不正确、有点正确、多数正确及完全正确,分数越高说明自我效能感越强。④随访后记录两组护理满意度,根据文献[10]对患儿及其家属从护理评价、矫正效果、医护人员的专业性、随访工作等方面进行评估,分为满意、部分满意、不满意三个级别,总满意度=(满意+部分满意)例数/总例数×100%。
关系、面型无改善,总有效率=(显效+有效)例数/总例数×100%。②分别于干预前后,采用锥形束CT(CBCT)图像[8]测量并记录两组前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度及下前牙唇倾度。③分别于干预前后记录两组自我效能感评分,采用一般自我效能感量表(GSES)[9]进行评估,共10个项目,包括解决问题能力、心理状态、社会能力等,分为完全不正确、有点正确、多数正确及完全正确,分数越高说明自我效能感越强。④随访后记录两组护理满意度,根据文献[10]对患儿及其家属从护理评价、矫正效果、医护人员的专业性、随访工作等方面进行评估,分为满意、部分满意、不满意三个级别,总满意度=(满意+部分满意)例数/总例数×100%。1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS 22.0 统计学软件进行数据分析,计量资料用均数±标准差(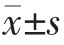 )表示,两组间比较采用t 检验;计数资料以率表示,组间比较采用χ2 检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
)表示,两组间比较采用t 检验;计数资料以率表示,组间比较采用χ2 检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 两组患儿总有效率的比较
观察组总有效率高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表1)。
表1 两组患儿总有效率的比较[n(%)]
.jpg)
2.2 两组患儿干预前后前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度及下前牙唇倾度的比较
干预前,两组前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度及下前牙唇倾度比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后,两组前牙覆盖及上切牙唇倾度均低于干预前,下前牙唇倾度均高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后,观察组前牙覆盖及上切牙唇倾度均低于对照组,下前牙唇倾度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表2)。
表2 两组干预前后前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度及下前牙唇倾度的比较(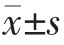 )
)
.jpg)
2.3 两组患儿干预前后自我效能感评分的比较
干预前,两组自我效能感评分比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后,两组自我效能感评分高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后,观察组自我效能感评分高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表3)。
表3 两组患儿干预前后自我效能感评分的比较(分,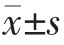 )
)
.jpg)
与本组干预前比较,#P<0.05
2.4 两组护理满意情况的比较
观察组护理总满意度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表4)。
表4 两组护理满意情况的比较[n(%)]
.jpg)
3 讨论
目前,错 畸形早期矫治的主要目的通过纠正下颌位置,改善口颌肌、咀嚼肌、口周肌功能,促进软组织恢复至正常功能,起到矫正错颌畸形的目的,通常采用辅助仪器矫正法,以改善利于牙颌、面部的正常发育,是临床上最常用的治疗手段之一,但其治疗过程缓慢,患儿不易配合,整体面部不够美观,长期下来可能会给患儿带来一定的心理负担,因此需要协助家属进行适当的心理护理来缓解其心理状态,增强治疗依从性。舌肌功能训练,包括弹舌、吸上腭、舌外伸、唇肌等训练,其主要优势有以下几点:①可减小上切牙唇倾度、增加下前牙唇倾度,使
畸形早期矫治的主要目的通过纠正下颌位置,改善口颌肌、咀嚼肌、口周肌功能,促进软组织恢复至正常功能,起到矫正错颌畸形的目的,通常采用辅助仪器矫正法,以改善利于牙颌、面部的正常发育,是临床上最常用的治疗手段之一,但其治疗过程缓慢,患儿不易配合,整体面部不够美观,长期下来可能会给患儿带来一定的心理负担,因此需要协助家属进行适当的心理护理来缓解其心理状态,增强治疗依从性。舌肌功能训练,包括弹舌、吸上腭、舌外伸、唇肌等训练,其主要优势有以下几点:①可减小上切牙唇倾度、增加下前牙唇倾度,使 关系逐渐趋于正常;②可强化舌体活动,增加舌肌力量,改善其灵活性,扩大活动范围,促进舌头感觉恢复;③可有效改善颌面异常,使得面部肌肉系统趋于正常。口腔本身就具有咀嚼、吞咽等功能,与口周、唇、舌、面部等多部位协同作用,支配下颌及颈椎关节肌肉,配合舌肌功能矫治,不仅可以锻炼舌肌,调控肌肉协调性,维持肌功能平衡,重建正常功能,改善牙弓、牙颌骨的异常形态,还可以促进消化腺分泌,使唾液、胃肠液分泌增多,改善机体消化功能,增进患儿食欲,促进营养吸收。因此适当的舌肌功能训练用于错颌畸形治疗中,可使牙齿排列及牙颌骨恢复正常水平,保持肌动力平衡,除此之外,对于因神经系疾病所引起的语言不清和舌运动障碍有良好的治疗作用[11]。
关系逐渐趋于正常;②可强化舌体活动,增加舌肌力量,改善其灵活性,扩大活动范围,促进舌头感觉恢复;③可有效改善颌面异常,使得面部肌肉系统趋于正常。口腔本身就具有咀嚼、吞咽等功能,与口周、唇、舌、面部等多部位协同作用,支配下颌及颈椎关节肌肉,配合舌肌功能矫治,不仅可以锻炼舌肌,调控肌肉协调性,维持肌功能平衡,重建正常功能,改善牙弓、牙颌骨的异常形态,还可以促进消化腺分泌,使唾液、胃肠液分泌增多,改善机体消化功能,增进患儿食欲,促进营养吸收。因此适当的舌肌功能训练用于错颌畸形治疗中,可使牙齿排列及牙颌骨恢复正常水平,保持肌动力平衡,除此之外,对于因神经系疾病所引起的语言不清和舌运动障碍有良好的治疗作用[11]。
 畸形早期矫治的主要目的通过纠正下颌位置,改善口颌肌、咀嚼肌、口周肌功能,促进软组织恢复至正常功能,起到矫正错颌畸形的目的,通常采用辅助仪器矫正法,以改善利于牙颌、面部的正常发育,是临床上最常用的治疗手段之一,但其治疗过程缓慢,患儿不易配合,整体面部不够美观,长期下来可能会给患儿带来一定的心理负担,因此需要协助家属进行适当的心理护理来缓解其心理状态,增强治疗依从性。舌肌功能训练,包括弹舌、吸上腭、舌外伸、唇肌等训练,其主要优势有以下几点:①可减小上切牙唇倾度、增加下前牙唇倾度,使
畸形早期矫治的主要目的通过纠正下颌位置,改善口颌肌、咀嚼肌、口周肌功能,促进软组织恢复至正常功能,起到矫正错颌畸形的目的,通常采用辅助仪器矫正法,以改善利于牙颌、面部的正常发育,是临床上最常用的治疗手段之一,但其治疗过程缓慢,患儿不易配合,整体面部不够美观,长期下来可能会给患儿带来一定的心理负担,因此需要协助家属进行适当的心理护理来缓解其心理状态,增强治疗依从性。舌肌功能训练,包括弹舌、吸上腭、舌外伸、唇肌等训练,其主要优势有以下几点:①可减小上切牙唇倾度、增加下前牙唇倾度,使 关系逐渐趋于正常;②可强化舌体活动,增加舌肌力量,改善其灵活性,扩大活动范围,促进舌头感觉恢复;③可有效改善颌面异常,使得面部肌肉系统趋于正常。口腔本身就具有咀嚼、吞咽等功能,与口周、唇、舌、面部等多部位协同作用,支配下颌及颈椎关节肌肉,配合舌肌功能矫治,不仅可以锻炼舌肌,调控肌肉协调性,维持肌功能平衡,重建正常功能,改善牙弓、牙颌骨的异常形态,还可以促进消化腺分泌,使唾液、胃肠液分泌增多,改善机体消化功能,增进患儿食欲,促进营养吸收。因此适当的舌肌功能训练用于错颌畸形治疗中,可使牙齿排列及牙颌骨恢复正常水平,保持肌动力平衡,除此之外,对于因神经系疾病所引起的语言不清和舌运动障碍有良好的治疗作用[11]。
关系逐渐趋于正常;②可强化舌体活动,增加舌肌力量,改善其灵活性,扩大活动范围,促进舌头感觉恢复;③可有效改善颌面异常,使得面部肌肉系统趋于正常。口腔本身就具有咀嚼、吞咽等功能,与口周、唇、舌、面部等多部位协同作用,支配下颌及颈椎关节肌肉,配合舌肌功能矫治,不仅可以锻炼舌肌,调控肌肉协调性,维持肌功能平衡,重建正常功能,改善牙弓、牙颌骨的异常形态,还可以促进消化腺分泌,使唾液、胃肠液分泌增多,改善机体消化功能,增进患儿食欲,促进营养吸收。因此适当的舌肌功能训练用于错颌畸形治疗中,可使牙齿排列及牙颌骨恢复正常水平,保持肌动力平衡,除此之外,对于因神经系疾病所引起的语言不清和舌运动障碍有良好的治疗作用[11]。本研究结果显示,观察组总有效率高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。提示舌肌功能训练联合心理疏导应用于错 畸形患儿早期矫治中,矫正效果良好,能显著改善前牙覆盖、
畸形患儿早期矫治中,矫正效果良好,能显著改善前牙覆盖、 关系及面型,分析原因可能是通过医护人员与家属协助完成舌肌功能训练,能强化患儿舌部肌肉,恢复牙颌面正常功能,提高肌动力平衡,达到矫正畸形的作用;还可养成闭唇习惯,使口周骨肉功能达到平衡,从而改善颅面
关系及面型,分析原因可能是通过医护人员与家属协助完成舌肌功能训练,能强化患儿舌部肌肉,恢复牙颌面正常功能,提高肌动力平衡,达到矫正畸形的作用;还可养成闭唇习惯,使口周骨肉功能达到平衡,从而改善颅面 美观,与吕娟等[12]的研究结果一致。本研究结果显示,干预前,两组前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度及下前牙唇倾度比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后,两组前牙覆盖及上切牙唇倾度均低于干预前,下前牙唇倾度均高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后,观察组前牙覆盖及上切牙唇倾度均低于对照组,下前牙唇倾度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。提示经过适当的舌肌功能训练,可有效促进上下颌骨发育及牙弓增长,同时配合矫正器使用,可使牙颌恢复正常位置,与朱俊贤等[13]及张维琼等[14]的研究结果具有一致性;此外,干预前,两组自我效能感评分比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后,两组自我效能感评分高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后,观察组自我效能感评分高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组护理总满意度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。提示舌肌功能训练联合心理干预应用于错
美观,与吕娟等[12]的研究结果一致。本研究结果显示,干预前,两组前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度及下前牙唇倾度比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后,两组前牙覆盖及上切牙唇倾度均低于干预前,下前牙唇倾度均高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后,观察组前牙覆盖及上切牙唇倾度均低于对照组,下前牙唇倾度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。提示经过适当的舌肌功能训练,可有效促进上下颌骨发育及牙弓增长,同时配合矫正器使用,可使牙颌恢复正常位置,与朱俊贤等[13]及张维琼等[14]的研究结果具有一致性;此外,干预前,两组自我效能感评分比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后,两组自我效能感评分高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后,观察组自我效能感评分高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组护理总满意度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。提示舌肌功能训练联合心理干预应用于错 畸形患儿早期矫治中,一方面可有效提升患儿自我解决问题能力,改善消极的心理状态,提升社会能力及生活质量;另一方面,通过医护人员与家属协助患儿完成一系列功能训练,在一定程度上可促进护患和谐,提高护理效果,吕冰洁等[15]的研究结论也证实了这一点。
畸形患儿早期矫治中,一方面可有效提升患儿自我解决问题能力,改善消极的心理状态,提升社会能力及生活质量;另一方面,通过医护人员与家属协助患儿完成一系列功能训练,在一定程度上可促进护患和谐,提高护理效果,吕冰洁等[15]的研究结论也证实了这一点。
 畸形患儿早期矫治中,矫正效果良好,能显著改善前牙覆盖、
畸形患儿早期矫治中,矫正效果良好,能显著改善前牙覆盖、 关系及面型,分析原因可能是通过医护人员与家属协助完成舌肌功能训练,能强化患儿舌部肌肉,恢复牙颌面正常功能,提高肌动力平衡,达到矫正畸形的作用;还可养成闭唇习惯,使口周骨肉功能达到平衡,从而改善颅面
关系及面型,分析原因可能是通过医护人员与家属协助完成舌肌功能训练,能强化患儿舌部肌肉,恢复牙颌面正常功能,提高肌动力平衡,达到矫正畸形的作用;还可养成闭唇习惯,使口周骨肉功能达到平衡,从而改善颅面 美观,与吕娟等[12]的研究结果一致。本研究结果显示,干预前,两组前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度及下前牙唇倾度比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后,两组前牙覆盖及上切牙唇倾度均低于干预前,下前牙唇倾度均高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后,观察组前牙覆盖及上切牙唇倾度均低于对照组,下前牙唇倾度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。提示经过适当的舌肌功能训练,可有效促进上下颌骨发育及牙弓增长,同时配合矫正器使用,可使牙颌恢复正常位置,与朱俊贤等[13]及张维琼等[14]的研究结果具有一致性;此外,干预前,两组自我效能感评分比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后,两组自我效能感评分高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后,观察组自我效能感评分高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组护理总满意度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。提示舌肌功能训练联合心理干预应用于错
美观,与吕娟等[12]的研究结果一致。本研究结果显示,干预前,两组前牙覆盖深度、上切牙唇倾度及下前牙唇倾度比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后,两组前牙覆盖及上切牙唇倾度均低于干预前,下前牙唇倾度均高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后,观察组前牙覆盖及上切牙唇倾度均低于对照组,下前牙唇倾度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。提示经过适当的舌肌功能训练,可有效促进上下颌骨发育及牙弓增长,同时配合矫正器使用,可使牙颌恢复正常位置,与朱俊贤等[13]及张维琼等[14]的研究结果具有一致性;此外,干预前,两组自我效能感评分比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);干预后,两组自我效能感评分高于干预前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);干预后,观察组自我效能感评分高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组护理总满意度高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。提示舌肌功能训练联合心理干预应用于错 畸形患儿早期矫治中,一方面可有效提升患儿自我解决问题能力,改善消极的心理状态,提升社会能力及生活质量;另一方面,通过医护人员与家属协助患儿完成一系列功能训练,在一定程度上可促进护患和谐,提高护理效果,吕冰洁等[15]的研究结论也证实了这一点。
畸形患儿早期矫治中,一方面可有效提升患儿自我解决问题能力,改善消极的心理状态,提升社会能力及生活质量;另一方面,通过医护人员与家属协助患儿完成一系列功能训练,在一定程度上可促进护患和谐,提高护理效果,吕冰洁等[15]的研究结论也证实了这一点。综上所述,舌肌功能训练联合心理疏导应用于错 畸形中,矫正效果良好,能有效改善前牙覆盖、
畸形中,矫正效果良好,能有效改善前牙覆盖、 关系及自我效能感,值得临床推广。
关系及自我效能感,值得临床推广。
 畸形中,矫正效果良好,能有效改善前牙覆盖、
畸形中,矫正效果良好,能有效改善前牙覆盖、 关系及自我效能感,值得临床推广。
关系及自我效能感,值得临床推广。[参考文献]
[1]宋卫军,郑琳琳,李寒,等.安氏Ⅰ类和安氏Ⅱ类错 畸形正畸后上切牙牙根吸收的临床研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2019,35(3):40-43.
畸形正畸后上切牙牙根吸收的临床研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2019,35(3):40-43.
 畸形正畸后上切牙牙根吸收的临床研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2019,35(3):40-43.
畸形正畸后上切牙牙根吸收的临床研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2019,35(3):40-43.[2]许霞,陈宝勇,程丽.无托槽隐形矫治器治疗成人牙周病继发错 畸形的临床研究[J].全科口腔医学电子杂志,2018,5(20):102-104.
畸形的临床研究[J].全科口腔医学电子杂志,2018,5(20):102-104.
 畸形的临床研究[J].全科口腔医学电子杂志,2018,5(20):102-104.
畸形的临床研究[J].全科口腔医学电子杂志,2018,5(20):102-104.[3]吴剑豪.自锁托槽矫正技术在安氏Ⅰ类错 畸形合并牙周炎患儿中的应用[J].中国乡村医药,2018,25(6):24-25.
畸形合并牙周炎患儿中的应用[J].中国乡村医药,2018,25(6):24-25.
 畸形合并牙周炎患儿中的应用[J].中国乡村医药,2018,25(6):24-25.
畸形合并牙周炎患儿中的应用[J].中国乡村医药,2018,25(6):24-25.[4]吴可,谷妍,周明智,等.配合前牙种植支抗矫治安氏Ⅱ2错()畸形的疗效研究[J].口腔医学,2019,39(6):514-518.
[5]宋艳.护理干预配合舌肌功能训练在错 畸形患儿早期矫正中的应用[J].实用临床医药杂志,2018,22(8):114-116.
畸形患儿早期矫正中的应用[J].实用临床医药杂志,2018,22(8):114-116.
 畸形患儿早期矫正中的应用[J].实用临床医药杂志,2018,22(8):114-116.
畸形患儿早期矫正中的应用[J].实用临床医药杂志,2018,22(8):114-116.[6]李小兵.儿童早期肌功能训练与错 畸形预防矫治[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2015,42(3):249-254.
畸形预防矫治[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2015,42(3):249-254.
 畸形预防矫治[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2015,42(3):249-254.
畸形预防矫治[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2015,42(3):249-254.[7]张艳艳,叶丹,郭维华.咬合诱导与功能矫治在儿童早期错 畸形矫治中的应用[J].口腔生物医学,2016,7(4):204-210.
畸形矫治中的应用[J].口腔生物医学,2016,7(4):204-210.
 畸形矫治中的应用[J].口腔生物医学,2016,7(4):204-210.
畸形矫治中的应用[J].口腔生物医学,2016,7(4):204-210.[8]史真,滕延萍.口面肌功能治疗在安氏Ⅱ1类错()早期矫治中的应用[J].中华口腔正畸学杂志,2017,24(1):20-25.
[9]金婕,陈钰文,朱玉,等.FRⅡ型功能矫治器与肌激动器对儿童安氏Ⅱ1类错()矫治效果对比研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2015,8(11):668-671.
[10]郑学汜.固定正畸治疗矫治前后错颌畸形严重程度与患者满意度相关研究[J].局解手术学杂志,2013,22(5):513-514.
[11]王珊珊,顾莹,刘敏,等.舌压抗阻反馈训练联合神经肌肉电刺激治疗神经性吞咽障碍的疗效观察[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2020,42(4):322-324.
[12]吕娟,高子龙,朱有家.MRC用于早期错()畸形阻断性矫治的效果分析[J].医学信息,2018,31(11):180-182.
[13]朱俊贤,毛慧敏,李娇,等.基于锥形束CT分析安氏Ⅱ类1分类与安氏Ⅲ类错 畸形上颌切牙区牙槽骨形态特征的研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2020,13(2):100-105.
畸形上颌切牙区牙槽骨形态特征的研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2020,13(2):100-105.
 畸形上颌切牙区牙槽骨形态特征的研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2020,13(2):100-105.
畸形上颌切牙区牙槽骨形态特征的研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2020,13(2):100-105.[14]张维琼,许红苗,陈伟仕.MRC 矫治器联合肌功能训练在儿童错 畸形的应用[J].浙江临床医学,2018,20(8):1388-1390.
畸形的应用[J].浙江临床医学,2018,20(8):1388-1390.
 畸形的应用[J].浙江临床医学,2018,20(8):1388-1390.
畸形的应用[J].浙江临床医学,2018,20(8):1388-1390.[15]吕冰洁,赵常晓.咬合诱导与功能矫治在儿童早期错畸形矫治中的应用[J].全科口腔医学电子杂志,2018,5(36):41-42.
Effect of tongue muscle functional training combined with psychological counseling on self-efficacy of children undergoing early treatment for malocclusion
HE Jia
Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Dalian Stomatological Hospital, Liaoning Province, Dalian 116021, China
Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Dalian Stomatological Hospital, Liaoning Province, Dalian 116021, China
[Abstract]Objective To explore effect of tongue muscle functional training combined with psychological counseling on self-efficacy of children undergoing early treatment for malocclusion.Methods A total of 136 cases with malocclusion who were admitted to the Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Dalian Stomatological Hospital from August 2018 to December 2019 were selected.They were divided into an observation group (68 cases) and a control group (68 cases) according to the random number table method.Both groups were given psychological counseling during early treatment,and the observation group was additionally given 8 weeks of tongue muscle functional training.Correction effects of the two groups were evaluated, and the anterior teeth coverage depth, upper incisor inclination, lower anterior teeth inclination, self-efficacy changes and nursing satisfaction were recorded before and after treatment.Results The total effective rate of the observation group was higher than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).Before intervention, there were no statistically significant differences in anterior teeth coverage depth, upper incisor inclination and lower anterior teeth inclination between the two groups (P>0.05).After intervention, the anterior tooth coverage and upper incisor inclination of both groups were smaller than those before intervention, while the lower anterior teeth inclination was larger than that before intervention, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05).After intervention, the anterior tooth coverage and upper incisor inclination in the observation group was lower than that in the control group, and the lower anterior teeth inclination was higher than that in the control group, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05).Before intervention, there was no significant difference in self-efficacy score between the two groups (P<0.05).After intervention, the self-efficacy scores of the two groups were higher than those before intervention, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).After intervention, that self-efficacy score of the observation group was higher than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).The total satisfaction degree of nursing care in the observation group was higher than that in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).Conclusion Applying tongue muscle functional training in psychological nursing of patients undergoing early treatment for malocclusion can improve the anterior teeth coverage depth, upper incisor inclination and lower anterior teeth inclination as well as the patient′s self-efficacy.It can also promote the development of harmonious nurse-patient relationship.
[Key words]Tongue muscle functional training;Psychological counseling;Malocclusion;Early treatment;Self-efficacy
[中图分类号]R246.8
[文献标识码]A
[文章编号]1674-4721(2021)3(b)-0133-04
(收稿日期:2020-07-02)