微创经皮锁钉钢板固定与传统固定法在四肢骨折患者中的临床应用效果比较
杨永华 胡 斌 杨海龙 杨敏捷 高展望
江西省九江市第一人民医院骨科,江西九江 332000
[摘要]目的探讨微创经皮锁钉钢板固定与传统固定法在四肢骨折患者中的临床应用效果比较。方法 选取2017年5月至2020年5月九江市第一人民医院收治的82例四肢骨折患者为研究对象,采用随机数字表法分为观察组与对照组,每组各41例。观察组采用微创经皮锁钉钢板进行内固定治疗,对照组则采用传统钢板螺钉进行内固定治疗。比较两组患者的临床疗效、手术相关指标、血液流变学指标及并发症发生情况。结果 观察组的临床总有效率为95.1%,高于对照组的80.5%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。观察组患者的手术时间、住院时间短于对照组,术中出血量少于对照组,切口长度短于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。两组术前全血黏度、血浆纤维蛋白原、红细胞沉降率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);两组术后3 d的全血黏度、血浆纤维蛋白原、红细胞沉降率均低于本组术前,且观察组术后3 d的全血黏度、血浆纤维蛋白原、红细胞沉降率均低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。观察组的并发症总发生率为7.3%,低于对照组的24.4%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 微创经皮锁钉钢板在四肢骨折患者中的临床疗效显著优于传统钢板螺钉固定法,能够有效改善患者局部血流循环,从而促使患者的骨折早期愈合,有助于患者早日出院。
[关键词]微创经皮锁钉钢板;四肢骨折;临床疗效;血液流变学
随着社会发展,汽车保有量不断增加,交通事故发生率也明显提高,这导致骨折发生率也随之有明显的增加[1]。四肢骨折为骨科常见疾病,过去常使用切开复位固定手术进行治疗,但是随着我国微创手术的推广,微创经皮锁钉钢板固定法在四肢骨折患者的临床治疗中表现出了较好的应用效果,该术式具有创伤小、愈合时间短且并发症发生率较低等优势而受到广泛的使用[2]。目前关于微创经皮锁钉钢板固定法与传统固定法对四肢骨折疗效比较的研究虽有报道,但多以临床观察为主[3],对于两种术式血液流变学指标的研究较少,分析两种术式对血液流变学指标的影响有助于反映不同术式对患者机体创伤程度,因此本研究旨在通过对微创经皮锁定钢板和传统固定方法在四肢骨折患者中的临床疗效及对血液流变学的影响,以期为临床上两种术式的选择提供参考依据。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2017年5月至2020年5月九江市第一人民医院收治的82例四肢骨折患者,按随机数字表法分为观察组与对照组,每组各41例。对照组中,男27例,女 14 例;年龄 19~60 岁,平均(41.95±7.88)岁;骨折位置:上肢骨折22例,下肢骨折19例;骨折原因:交通事故21例,高空坠落13例,摔倒5例,其他2例。研究组中,男25例,女16例;年龄18~60岁,平均(43.05±7.19)岁;骨折位置:上肢骨折25例,下肢骨折16例;骨折原因:交通事故20例,高空坠落13例,摔倒6例,其他2例。两组的一般资料的比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。纳入标准:①经影像学检查确诊为四肢骨折者;②符合内固定手术指征者;③患者神志清醒,可配合相关治疗及检查;④患者已签署知情同意书。排除标准:①凝血功能异常者;②骨质疏松以及骨性疾病患者;③孕妇及乳母。本研究经医院医学伦理委员会审核及批准。
1.2 方法
对照组行传统内固定,视病情选择麻醉方式,术前制订手术方案,骨折断端在进行牵引复位后再行内固定。观察组行微创经皮锁钉钢板内固定治疗,以腰麻联合硬膜外麻醉,取仰卧位并注意保暖,用骨剥向骨折临近部位的骨膜附着的软组织进行剥离,建立皮下通道,并以健肢为对照,在Siremobil Compact L型C形臂机(德国西门子公司)下进行复位对线和对位,并使用螺钉固定。若骨折部位在跟骨,需要使用跟骨钛板固定;若骨折部位在关节周围,需要通过近关节解剖型锁定加压钢板进行固定。
1.3 观察指标及评价标准
比较两组患者的临床疗效,手术相关指标、血液流变学指标及并发症发生情况。①疗效评价:术后30 d参照文献[4]以X线检查结果进行疗效评价。显效:骨折完全愈合;有效:骨折部位可见连续性骨痂;无效:X线检查仍有明显的骨折线。总有效率=(显效+有效)例数/总例数×100%。②手术相关指标:收集两组患者手术时间、术中出血量、住院时间及切口长度。③血液流变学指标:在术前、术后3 d后抽取患者空腹外周静脉血以血液流变仪对患者全血黏度、血浆纤维蛋白原以及红细胞沉降率进行检测。④记录两组患者的并发症发生情况。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS 16.0统计学软件进行统计学分析,计量资料用均数±标准差(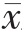 ±s)表示,两组间比较采用t检验;计数资料用率表示,采用χ2检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
±s)表示,两组间比较采用t检验;计数资料用率表示,采用χ2检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
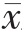 ±s)表示,两组间比较采用t检验;计数资料用率表示,采用χ2检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
±s)表示,两组间比较采用t检验;计数资料用率表示,采用χ2检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。2 结果
2.1 两组患者临床疗效的比较
观察组的临床总有效率高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表 1)。
表1 两组患者临床疗效的比较[n(%)]
.jpg)
2.2 两组患者手术相关指标的比较
观察组患者的手术时间、住院时间短于对照组,术中出血量少于对照组,切口长度短于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表 2)。
表2 两组患者手术相关指标的比较(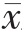 ±s)
±s)
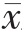 ±s)
±s).jpg)
2.3 两组患者手术前后血液流变学指标的比较
两组患者术前全血黏度、血浆纤维蛋白原、红细胞沉降率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。两组患者术后3 d的全血黏度、血浆纤维蛋白原、红细胞沉降率均低于本组术前,且观察组术后3 d的全血黏度、血浆纤维蛋白原、红细胞沉降率均低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表 3)。
表3 两组患者手术前后血液流变学指标的比较(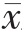 ±s)
±s)
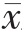 ±s)
±s).jpg)
与本组术前比较,aP<0.05;与对照组比较,bP<0.05
2.4 两组患者并发症总发生率的比较
观察组的并发症总发生率低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表 4)。
表4 两组患者并发症总发生率的比较[n(%)]
.jpg)
3 讨论
因传统内固定术需对骨折部位周围肌肉、筋膜和软组织进行剥离而致其并发症发生率较高[5-6]。传统钢板固定仅通过钢板与骨骼表面之间摩擦而固定骨折部位,缺乏必要的锁定结构,在术中需紧压骨表,导致钢板下骨骼容易出现缺血性坏死,另外传统固定术对骨折部位周围骨膜与软组织剥离较为严重,对患者机体造成严重的创伤,同时增加了安装钢板时所产生的医源性损伤概率,进而破坏了骨折端血运,给骨折愈合带来一定负面影响[7-9]。随着技术的发展,对于四肢骨折的手术方案已向生物力学方向转变,加上微创技术的引入使四肢骨折内固定术的临床疗效得到了明显提升[10-11]。
微创经皮锁定钢板仅需在骨折部位行小切口,然后建立皮下通道,将钢板移动到骨折部位,相对于传统的内固定方式对患者骨折部位周围组织的剥离较少,可有效减少周围组织的损伤,加速骨折的愈合,使固定效果得到明显的提高。本次研究结果显示,观察组患者的手术时间、住院时间短于对照组,术中出血量少于对照组,切口长度短于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),与上述观点相一致。微创经皮锁定钢板的优点在于:①微创方式较传统内固定方式低具有较高的安全性。可能与微创方式内固定术在钢板置入及手术部位剥离时对患者创伤较小,避免因大面积创伤给患者带来的并发症。经皮锁钉钢板能够减小对患者机体的创伤,从而改善患者的预后情况有关[12]。②肌肉损伤小。由于皮下通道的建立能够减小对骨折周围组织剥离造成的损伤,有助于降低切口周围疼痛的发生率[13]。此外,经皮锁钉钢板对患者造成的损伤小,能够促使患者早日愈合。本研究中观察组并发症发生率低于对照组也证实了此观点。③术中出血量少。经皮下通道的方式无需切断大量血管,能够保持局部血液循环的稳定性,而减小出血量[14]。
血液流变学主要是评价血液循环状态的重要指标,可有效观察骨折部位血液循环的情况。本研究结果显示,观察组对患者血液流变学指标影响更小(P<0.05),这可能是因为观察组所采用的微创锁钉钢板和生物力学原理相符且手术为微创的方式,对机体创伤较小,无需对骨膜进行剥离也能最大限度的减少对骨折端血运造成的影响而减小患者血流动力学参数的影响,有利于促进骨折端微循环的恢复,为骨折的愈合提供了便利的条件[15]。
综上所述,微创经皮锁钉钢板在四肢骨折患者中的临床疗效显著优于传统钢板螺钉固定法,能够有效改善患者局部血流循环,从而促使患者的骨折早期愈合,有助于患者早日出院。
[参考文献]
[1]付常国,贾坤,李涛,等.四肢骨折锁定钢板内固定存在的问题及对策[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016,31(3):325-327.
[2]Enninghorst N,Hardy Bm,Sisak K,et al.Tissue oxygen saturation changes during intramedullary nailing of lower-limb fractures[J].J Trauma Acute Care Surg,2013,74(1):123-127.
[3]阎海威,胡居正,杨英,等.微创经皮骨盆前环内固定治疗不稳定性前环损伤的疗效及早期并发症分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(13):826-832.
[4]Vickas J,Mudabbir MS,Kamal SK,et al.The functional and radiological outcome of minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis(MIPPO)in treatment of distal meta-physeal fractures of tibia[J].Int J Orthop,2020,6(1):995-998.
[5]刘晓军.微创经皮锁定加压钢板内固定对四肢骨折患者术后视觉模拟评分及骨折愈合时间的影响[J].山西医药杂志,2019,48(5):593-595.
[6]刘辉均,丁茂乾,任诗松.经皮微创钢板接骨术技术结合锁定加压钢板内固定在四肢骨折创伤病人中的临床应用及对生活质量的影响[J].临床外科杂志,2020,28(1):78-81.
[7]Noh YM,Kim DR,Kim CH,et al.Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis via a deltoidsplitting approach with strut allograft for the treatment of displaced 3-or 4-part proximal humeral fractures[J].Clin Should Elbow,2018,21(4):220-225.
[8]Akhtar RR,Ahmed R,Khan AN,et al.Outcome of Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis Technique for Management of Extra Articular Distal Tibial Fractures[J].J Rawalpindi Med Col,2021,25(1):107-111.
[9]Vickas J,Mudabbir MS,Kamal SKM,et al.Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis(MIPPO)in treatment of distal meta-physeal fractures of tibia:A study on Complications[J].Int J Orthop,2020,6(1):999-1002.
[10]Wang B,Zhao Y,Wang Q,et al.Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis versus intramedullary nail fixation for distal tibial fractures:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].J Orthopa Surg Res,2019,14(1):1-9.
[11]Barcellos RR,Correia DPD,Farina AP,et al.Fracture resistance of endodontically treated teeth restored with intra-radicular post:The effects of post system and dentine thickness[J].J Biomech,2013,46(15):2572-2577.
[12]Hambli R,Allaoui S.A robust 3D finite element simulation of human proximal femur progressive fracture under stance load with experimental validation[J].Ann Biomed Eng,2013,41(12):2515-2527.
[13]Tassani S,Matsopoulos G K,Baruffaldi F,et al.3D identification of trabecular bone fracture zone using an automatic image registration scheme:A validation study[J].J Biomech,2015,45(11):2035-2040.
[14]Hambli R,Bettamer A,Allaoui S,et al.Finite element prediction of proximal femur fracture pattern based on orthotropic behaviour law coupled to quasi-brittle damage[J].Med Eng Phys,2015,34(2):202-210.
[15]Wright DA,Nam D,Whyne CM,et al.A comparison of stereology,structural rigidity and a novel 3D failure surface analysis method in the assessment of torsional strength and stiffness in a mouse tibia fracture model[J].J Biomech,2015,45(13):2236-2240.
Comparison of clinical effects between minimally invasive percutaneous locking compression plate fixation and traditional fixation in patients with limb fractures
YANG Yong-huaHU Bin YANG Hai-longYANG Min-jie GAO Zhan-wang
Department of Orthopedics,Jiujiang First People′s Hospital,Jiangxi Province,Jiujiang 332000,China
Department of Orthopedics,Jiujiang First People′s Hospital,Jiangxi Province,Jiujiang 332000,China
[Abstract]Objective To investigate comparison of clinical effects between minimally invasive percutaneous locking compression plate fixation and traditional fixation in patients with limb fractures.Methods A total of 82 patients with limb fractures admitted to our hospital from May 2017 to May 2020 were selected as the research subjects.They were divided into an observation group and a control group by a random number table,with 41 cases in each group.Patients in the observation group were treated with minimally invasive percutaneous locking compression plate for internal fixation,while patients in the control group were treated with traditional plate and screw for internal fixation.The clinical efficacy,operation-related indexes,hemorheology indexes,and complications were compared between the two groups.Results The clinical total overall response rate (95.1%)of the observation group was higher than that of the control group accounting for 80.5%,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).The surgical time and hospital stay of the observation group were shorter than those of the control group,the intraoperative blood loss of the observation group was less than that of the control group,the incision length of the observation group was shorter than that of the control group,the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).There was no significant difference in whole blood viscosity,plasma fibrinogen or erythrocyte sedimentation rate between the two groups before surgery (P>0.05).The whole blood viscosity,plasma fibrinogen,and erythrocyte sedimentation rate of the observation group were all lower than before surgery,the whole blood viscosity,plasma fibrinogen,and erythrocyte sedimentation rate of the observation group three days after surgery were all lower than those of the control group,the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).The total complication rate (7.3%)of the observation group was lower than that of the control group accounting for 24.4%,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).Conclusion The clinical efficacy of minimally invasive percutaneous locking compression plate in patients with limb fractures is much better than that of traditional plate and screw fixation,and it can effectively improve the local blood circulation of patients to promote the early healing of the fracture of patients,and is conducive to early discharge.
[Key words]Minimally invasive percutaneous locking compression plate;Limb fracture;Clinical efficacy;Hemorheology
[中图分类号]R683.4
[文献标识码]A
[文章编号]1674-4721(2021)11(b)-0075-04
[基金项目]江西省卫生计生委科技计划项目(20167094)。
[作者简介]杨永华(1974-),男,江西新余人,硕士,副主任医师,研究方向:临床骨科。
(收稿日期:2021-04-13)