双侧胸横肌平面阻滞对心脏外科手术患儿术后快速康复的影响
李晴晴 方 印 张斯璧 魏国华 尤纱纱▲
南京医科大学第一附属医院麻醉与围术期医学科,江苏南京 210029
[摘要]目的 探讨超声引导下双侧胸横肌平面(TTP)阻滞对减轻心脏外科手术患儿术后疼痛的有效性和安全性。方法 选择2020年1月至2020年12月于南京医科大学第一附属医院择期行胸骨正中切口室缺修补术的50例患儿,采用随机数字表法将其分为TTP组和对照组,每组各25例。TTP组患儿手术后在超声引导下平面内进针技术将0.375%罗哌卡因注射在双侧肋间内肌和胸横肌之间的平面,对照组不进行神经阻滞。比较两组术后改良目的疼痛评分(MOPS)、术中和术后24 h芬太尼用量、术后机械通气时间、ICU停留时间及住院时间,观察TTP阻滞相关不良事件的发生情况。结果 TTP组术后6、8、12、24 h的MOPS低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);TTP组术后48 h的MOPS高于本组术后6 h,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。TTP组术后24 h芬太尼用量少于对照组,TTP组术后机械通气时间、ICU停留时间短于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。两组术中芬太尼用量以及住院时间比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。TTP组未出现TTP阻滞相关不良事件。结论 超声引导下双侧TTP阻滞可安全有效地应用于心脏外科手术患儿术后镇痛,促进患儿术后快速康复。
[关键词]胸横肌平面阻滞;改良目的疼痛评分;小儿心脏外科;罗哌卡因
对于接受心内直视手术的患儿来讲,胸骨正中切口会引起严重术后疼痛[1-2],可能导致灾难性后果,如高血压、缺氧、快速型心律失常、肺动脉高压危象等[3-5],因而适当的疼痛管理是至关重要的。在现代快通道心脏麻醉方案中,有效的术后疼痛管理有助于早期拔管,维持血流动力学的稳定性[6]。胸横肌平面(transversus thoracis muscle plane,TTP)阻滞[7]是将局麻药注射在胸横肌与肋间肌平面之间,提供前胸部的镇痛。本研究观察超声引导下TTP阻滞对减轻心脏手术患儿术后疼痛的临床效果及安全性。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选择2020年1月至2020年12月于南京医科大学第一附属医院择期行胸骨正中切口室缺修补术患儿50例,采用随机数字表法将患儿分为TTP组和对照组,每组各25例。TTP组中,男17例,女8例;年龄1~10 岁,平均(5.48±1.68)岁;体重 11.2~26.5 kg,平均(14.14±3.88)kg。 对照组中,男 15 例,女 10 例;年龄1~9 岁,平均(5.32±1.54)岁;体重 10.6~24.3 kg,平均(13.81±4.02)kg。两组患儿的性别、年龄、体重等一般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。本研究已获南京医科大学第一附属医院医学伦理委员会批准,参与本研究的患儿监护人均已签署知情同意书。
纳入标准:美国麻醉医师协会(the American Society of Anesthesiologists,ASA)分级为Ⅱ~Ⅲ级。 排除标准:①左室射血分数<35%;②酰胺类局部麻醉剂过敏;③胸部畸形不能行神经阻滞;④穿刺部位感染;⑤肝肾功能不全;⑥急诊手术;⑦二次开胸手术。剔除标准:①需延迟关胸;②术中发现合并其他心脏畸形。
1.2 方法
术前常规禁饮禁食,患儿入室后开放静脉通道,常规监测心电图(electrocardiogram,ECG)、脉搏血氧饱和度(pulse oxygen saturation,SpO2),无创血压。
1.2.1 TTP组 ①面罩预吸氧后行麻醉诱导:静脉注射咪达唑仑0.05 mg/kg(江苏恩华药业股份有限公司,生产批号:MD191205)、丙泊酚 2 mg/kg(Corden Pharma S.P.A,生产批号:X20056A)、芬太尼 6 μg/kg(宜昌人福药业有限责任公司,生产批号:01E00203)、顺式阿曲库铵0.15 mg/kg(江苏恒瑞医药股份有限公司,生产批号:191213AU),直至患儿意识消失、肌肉松弛,达到足够的麻醉深度后进行气管插管。②麻醉维持:丙泊酚 6~8 mg/(kg·h),顺式阿曲库铵 0.05~0.1 mg/(kg·h),间断推注芬太尼。③手术结束后即刻对TTP组患儿进行超声引导下双侧TTP阻滞,胸骨周围部位消毒铺巾,消毒高频线性超声探头,超声探头置于胸骨外侧1 cm的矢状面,从锁骨附近的第2肋到第5肋,计数肋软骨,将超声探头旋转至第4肋软骨和第5肋软骨之间,将0.375%罗哌卡因(总量2.5 mg/kg)(AstraZeneca AB,生产批号:9A079)注射在胸横肌和肋间内肌之间的平面,注药前注意回抽无血,避免血管内注射或血管损伤。
1.2.2 对照组患儿不进行神经阻滞所有患儿术后均入ICU进一步监护治疗。当患儿术后改良目的疼痛评分[8](modifified objective pain score,MOPS)≥4 分时,给予芬太尼1 μg/kg进行补救镇痛。
ICU拔管标准:患儿神志清楚;血流动力学稳定;呼吸频率规律、潮气量达到5~7 ml/kg;拔管前动脉血气及血清电解质正常。
1.3 观察指标及评价标准
比较两组术后 6、8、12、24、48 h 的 MOPS。 MOPS可用于评估8个月~13岁患儿的术后镇痛,主要指标包括哭闹、活动情况、情绪、姿态和口头表达5个方面,最小得分为0,最大得分为10,当MOPS评分<4分时,表明镇痛有效,评分越高,疼痛越剧烈。
比较两组术中和术后情况:包括术中和术后24 h芬太尼用量、术后机械通气时间、ICU停留时间及住院时间。术后机械通气时间定义为到达ICU至拔管时间。
观察TTP阻滞相关不良事件 (穿刺部位血肿、动静脉损伤、罗哌卡因过敏、气胸及穿刺部位感染)的发生情况。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS 22.0统计学软件进行数据分析,符合正态分布的计量资料用均数±标准差(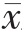 ±s)表示,两组间比较采用t检验,复测量数据采用重复测量方差分析,不符合正态分布者转换为正态分布后行统计学分析;计数资料采用率表示,组间比较采用χ2检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
±s)表示,两组间比较采用t检验,复测量数据采用重复测量方差分析,不符合正态分布者转换为正态分布后行统计学分析;计数资料采用率表示,组间比较采用χ2检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
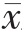 ±s)表示,两组间比较采用t检验,复测量数据采用重复测量方差分析,不符合正态分布者转换为正态分布后行统计学分析;计数资料采用率表示,组间比较采用χ2检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
±s)表示,两组间比较采用t检验,复测量数据采用重复测量方差分析,不符合正态分布者转换为正态分布后行统计学分析;计数资料采用率表示,组间比较采用χ2检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。2 结果
2.1 两组患儿术后不同时间点MOPS的比较
TTP组术后 6、8、12、24 h的 MOPS低于同时期对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);TTP组术后 48 h的MOPS高于本组术后6 h,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表 1)。
表1 两组患儿术后不同时间点MOPS的比较(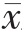 ±s)
±s)
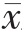 ±s)
±s).jpg)
与本组术后6 h比较,aP<0.05
2.2 两组患儿术中及术后情况的比较
TTP组术后24 h芬太尼用量少于对照组,TTP组术后机械通气时间、ICU停留时间短于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。两组术中芬太尼用量以及住院时间比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)(表 2)。
表2 两组患儿术中及术后情况的比较(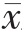 ±s)
±s)
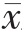 ±s)
±s).jpg)
2.3 TTP阻滞相关不良事件发生情况
TTP组未出现TTP阻滞相关不良事件。
3 讨论
研究表明,正中开胸手术后急性痛的发生率高达49%[9]。术后疼痛的严重程度影响气管拔管时间、术后血流动力学稳定及术后快速康复[10]。口服或静脉注射止痛药物是婴幼儿术后镇痛常用的方法,但有效镇痛所需的阿片类药物剂量可能会引起呼吸抑制、镇静以及胃肠道副作用(如恶心、呕吐和肠梗阻等)[11]。胸段硬膜外阻滞和椎旁阻滞技术为小儿心脏直视手术提供了良好的镇痛效果[12],但是,由于肝素化可能引起硬膜外血肿的发生、血流动力学不稳定、技术难度大、气胸等原因[13],限制了椎旁阻滞技术和胸段硬膜外阻滞技术在心脏直视手术中的应用,因而需要研究新的小儿心脏手术神经阻滞技术。本研究在胸骨旁第4肋软骨和第5肋软骨之间,将0.375%罗哌卡因(总量为2.5 mg/kg)注射在肋间肌和胸横肌之间的平面,超声下可以看到局麻药在胸横肌平面均匀扩散,可有效阻滞前胸壁区域的肋间神经皮支(T2~T6),提供前胸部镇痛。 本研究结果显示,TTP 组术后 6、8、12、24 h 的MOPS低于同时期对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);TTP组术后48 h的MOPS高于本组术后6 h,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);TTP组术后24 h芬太尼用量少于对照组,TTP组术后机械通气时间、ICU停留时间短于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);两组术中芬太尼用量以及住院时间比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);TTP组和对照组患儿术后48 h MOPS评分趋于一致,TTP组患儿术后48 h MOPS评分高于术后6 h MOPS评分,其原因是单次TTP阻滞镇痛持续时间有限。本研究结果显示,TTP阻滞组患儿均未出现神经阻滞相关并发症,TTP阻滞可能成为一种简单、有效、安全的术后镇痛方法推广到心脏手术患儿的围手术期管理。
TTP阻滞单独或复合全身麻醉的有效性与安全性已被国内外众多学者所证实[14-16],这也与当前所倡导的多模式镇痛的理念相符,既弥补了单一镇痛方式的缺点,减少了不良反应,又能够使患者达到更满意的镇痛效果,有利于术后康复,且安全性较高。Ueshima[14]报告了2例儿童使用TTP阻滞的病例,2例患儿行漏斗胸矫治术,结果表明TTP阻滞在儿童外科手术中对疼痛的处理非常有效。Fujii等[15]研究表明TTP组患者的满意度较高,且所有患者均未出现TTP阻滞相关并发症。Zhang等[16]的随机对照试验表明在心脏直视手术中应用双侧TTP阻滞可减少术中和术后芬太尼用量,缩短拔管时间、ICU停留时间,为缩短住院时间和促进术后快速康复奠定基础。这也与本研究结果相符。这些研究也均未出现TTP阻滞相关的严重并发症(气胸、穿刺部位血肿和局麻药中毒),因为TTP阻滞是浅表性的,且在超声引导直视下进行。
本研究也存在一定局限性,本研究TTP阻滞为单次神经阻滞,镇痛持续时间有限,因此需要进一步的研究来评估在胸横肌平面插入导管持续局部麻醉药输注以获得长期术后镇痛的效果。
综上所述,超声引导下TTP阻滞可安全有效地应用于经胸骨正中切口接受心脏手术的患儿,提供良好的术后镇痛,减少围手术期阿片类镇痛药的需求,促进早期拔管和术后快速康复。
[参考文献]
[1]Milgrom LB,Brooks JA,Qi R,et al.Pain levels experienced with activities after cardiac surgery[J].Am J Crit Care,2004,13(2):116-125.
[2]Ueshima H,Hara E,Marui T,et al.The ultrasound-guided transversus thocic muscle plane block is effective for the median sternotomy[J].J Clin Aesth,2016,28(2):83.
[3]Engelman DT,Ali WB,Williams JB,et al.Guidelines for Perioperative Care in Cardiac Surgery:Enhanced Recovery After Surgery Society Recommendations[J].JAMA Surg,2019,154(8):755-766.
[4]Bettex DA,Schmidlin D,Chassot PG,et al.Intrathecal sufentanil-morphine shortens the duration of intubation and improvesanalgesiainfast-trackcardiacsurgery[J].CanJAnaesth,2002,49(7):711-717.
[5]Beloeil H,Sulpice L.Peri-operative pain and its consequences[J].J Visc Surg,2016,153(6):15-18.
[6]Chaudhary V,Chauhan S,Choudhury M,et al.Parasternal intercostal block with ropivacaine for postoperative analgesia in pediatric patients undergoing cardiac surgery:a double-blind,randomized,controlled study[J].J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth,2012,26(3):439-442.
[7]Ueshima H,Kitamura A.Clinical experiences of ultrasound-guided transversus thoracic muscle plane block:a clinical experience[J].J Clin Anesth,2015,27(5):428-429.
[8]Zieliński J,Morawska-Kochman M,Zatoński T.Pain assessment and management in children in the postoperative period:A review of the most commonly used postoperative pain assessment tools,new diagnostic methods and the latest guidelines for postoperative pain therapy in children[J].Adv Clin Exp Med,2020,29(3):365-374.
[9]Huang AP,Sakata RK.Dor após esternotomia-revis o[Pain after sternotomy-review][J].Rev Bras Anestesiol,2016,66(4):395-401.
o[Pain after sternotomy-review][J].Rev Bras Anestesiol,2016,66(4):395-401.
 o[Pain after sternotomy-review][J].Rev Bras Anestesiol,2016,66(4):395-401.
o[Pain after sternotomy-review][J].Rev Bras Anestesiol,2016,66(4):395-401.[10]Abdelbaser II,Mageed NA.Analgesic efficacy of ultrasound guided bilateral transversus thoracis muscle plane block in pediatric cardiac surgery:a randomized,double-blind,controlled study[J].J Clin Anesth,2020,32(67):110-112.
[11]Fletcher D,Martinez V.Opioid-induced hyperalgesia in patients after surgery:A systematic review and a meta-analysis[J].Br J Anaesth,2014,112(6):991-1004.
[12]Fillinger MP,Yeager MP,Dodds TM,et al.Epidural anesthesia and analgesia:effects on recovery from cardiac surgery[J].J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth,2002,16(1):15-20.
[13]Ho AM,Chung DC,Joynt GM.Neuraxial blockade and hematoma in cardiac surgery:estimating the risk of a rare adverse event that has not(yet)occurred[J].Chest,2000,117(2):551-555.
[14]Ueshima H,Hiroshi O.Clinical experiences of Ultrasoundguided transversus thoracic muscle plane block for children[J].J Clin Anesth,2017,29(40):23.
[15]Fujii S,Roche M,Jones PM,et al.Transversus thoracis muscle plane block in cardiac surgery:a pilot feasibility study[J].Reg Anesth Pain Med,2019,44(5):556-560.
[16]ZhangY,Chen S,GongH,etal.EfficacyofBilateral Transversus Thoracis Muscle Plane Block in Pediatric Patients Undergoing Open Cardiac Surgery[J].J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth,2020,34(9):2430-2434.
Effect of bilateral transversus thoracis muscle plane block on fast track recovery after pediatric cardiac surgery
LI Qing-qing FANG Yin ZHANG Si-bi WEI Guo-hua YOU Sha-sha▲
Department of Anesthesia and Perioperative Medicine,the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University,Jiangsu Province,Nanjing 210029,China
Department of Anesthesia and Perioperative Medicine,the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University,Jiangsu Province,Nanjing 210029,China
[Abstract]Objective To explore the efficacy and safety of ultrasound bilateral thoracic transverse muscle plane(TTP)block on reducing postoperative pain in children with cardiac surgery.Methods A total of fifty pediatric patients in the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University from January 2020 to December 2020,and divided into the control group and the TTP group according to the random number table method,with 25 cases in each group.The TTP group received bilateral TTP blocks with 2.5 ml/kg 0.375% Ropivacaine,and the control group received no nerve block.The modified objective pain score (MOPS)in postoperative,the dose of Fentanyl used in interoperatively and postoperative 24 hours,the mechanical ventilation time in postoperative,the ICU stay time,and the length of stay were compared between the two groups,and observed the occurrence of adverse events related with TTP arrest.Results The MOPS of the TTP group was lower than of the control group in postoperative 6,8,12,24 hours,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).The MOPS of the TTP group in postoperative 24 hours was higher than that in postoperative 6 hours in the group,with statistically significant difference (P<0.05).The dose of Fentanyl used of the TTP group was less than that of the control group in postoperative 24 hours,the mechanical ventilation time in postoperative and the ICU stay time of the TTP group were shorter than those of the control group,with statistically significant differences(P<0.05).There were no statistically significant differences in the dose of Fentanyl used in interoperatively and the length of stay between the two groups (P>0.05).None of the children of the TTP group had any adverse events due to TTP block.Conclusion Ultrasound guided bilateral TTP block can be effectively and safely applied to postoperative analgesia in pediatric cardiac surgery,and promote rapid postoperative recovery.
[Key words]Transversus thoracis muscle plane;Modifified objective pain score;Pediatric cardiac surgery;Ropivacaine
[中图分类号]R614
[文献标识码]A
[文章编号]1674-4721(2021)11(a)-0125-04
▲通讯作者
(收稿日期:2021-07-17)