利拉鲁肽联合二甲双胍对初诊断超重/肥胖2型糖尿病患者体重、脂肪分布和β细胞功能的影响
叶静文1 梁慰强1 舒 毅1 邓嘉进2▲
1.南方医科大学附属南海医院内分泌科,广东佛山 528000;2.南方医科大学附属南海医院眼科,广东佛山 528000
[摘要]目的 探讨利拉鲁肽联合二甲双胍治疗对初诊断超重/肥胖2型糖尿病(T2DM)患者体重、脂肪分布与β细胞功能的影响。方法 选取2018年6月~2019年6月于我院治疗的80例初诊超重/肥胖T2DM患者作为研究对象,按照随机数字表法分为研究组和对照组,各40例。对照组给予二甲双胍治疗,研究组在对照组的基础上加用利拉鲁肽,治疗时间持续24周。比较两组患者治疗前后的体重、体重指数(BMI)、空腹血糖(FBG)、糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)、内脏脂肪面积(VFA)、皮下脂肪面积(SFA)和胰岛β细胞功能指数(HOMA-β)、胰岛素抵抗指数(HOMA-IR) 的变化。结果 两组患者治疗后的体重、BMI、FBG、HbA1c、HOMA-IR、VFA、SFA均低于治疗前,HOMA-β 高于治疗前,差异有统计学意义 (P<0.05);研究组患者治疗后的体重、BMI、FBG、HbA1c、HOMA-IR、VFA、SFA均低于对照组,HOMA-β 高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。两组患者治疗前后VFA与SFA 的比值(VSR)比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论 利拉鲁肽对初诊断超重/肥胖T2DM患者具有良好的降糖、降体重、改善脂肪分布及β细胞功能的作用。
[关键词]利拉鲁肽;2型糖尿病;体重;内脏脂肪;胰岛β细胞
2型糖尿病(type 2 diabetes mellitus,T2DM)是一种常见的慢性疾病,胰岛素抵抗和β细胞分泌缺陷是其发病机制的主要环节[1],而肥胖,尤其是腹部内脏脂肪(visceral adipose tissue,VAT)堆积与胰岛素抵抗增加有关[2],是T2DM 发展的主要危险因素[3]。胰高糖素样肽-1(glucagon-like peptide-1,GLP-1)是肠道产生的一种肠促胰岛素,其能刺激葡萄糖依赖的内源性胰岛素分泌,减少胰高糖素分泌,减缓胃的蠕动和排空,降低食欲和摄食量[4]。利拉鲁肽是一种与人GLP-1 具有97%的序列同源性的GLP-1 受体激动剂(glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist,GLP-1RA)[5]。本研究通过观察患者VAT 水平、胰岛功能及胰岛素抵抗的变化,评估利拉鲁肽对初诊超重/肥胖T2DM患者的疗效。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2018年6月~2019年6月于我院治疗的80例超重/肥胖T2DM患者作为研究对象。纳入标准:年龄为18~70岁;在1年内被诊断为T2DM,入组前未行降糖治疗或者曾不规律降糖治疗,入组时糖化血红蛋 白(glycosylated hemoglobin A1c,HbA1c)为7.0%~11.0%。排除标准:妊娠或哺乳期;对利拉鲁肽过敏;既往急性胰腺炎或慢性胰腺炎、炎症性肠病、胃肠手术包括胃分流术病史;甲状腺髓样癌史或家族史。根据随机数字表法将入组患者分为研究组和对照组,每组各40例。研究组中,男23例,女17例;年龄(51.85±12.43)岁。对照组中,男22例,女18例;年龄(51.78±12.69)岁。两组患者的性别、年龄比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。本研究经由我院医学伦理委员会审批,患者对本研究知情并签署知情同意书。
1.2 研究方法
两组患者均接受统一的糖尿病教育和生活方式指导。对照组患者给予二甲双胍(中美上海施贵宝制药有限公司,生产批号:ABL1013,规格:0.5 g/片)1.5~2.0 g/d 口服治疗。研究组患者在口服二甲双胍的基础上给予每天1次利拉鲁肽(丹麦诺和诺德公司,生产批号:JVGT863-1;规格:3 ml∶18 mg)皮下注射。利拉鲁肽初始剂量为0.6 mg/d(第1周),根据临床反应和副作用,在3周的时间内逐渐加量,1.2 mg/d(第2周)和1.8 mg/d(第3周)。两组患者均持续治疗24周,定期监测指尖血糖。低血糖被定义为指尖血糖<3.9 mmol/L。
1.3 观察指标
①比较两组患者治疗前后体重和体重指数(BMI)的变化情况。②治疗前后所有患者禁食8 h,采集静脉血,使用全自动生化仪(奥林巴斯AU5800)测定空腹血糖(fasting blood-glucose,FBG),采用化学发光法(新产业MAGLUMI 4000 Plus) 测定空腹胰岛素(fasting insulin,FINS),采用高压液相色谱法(爱科来AMADS) 测定HbA1c。③以胰岛β细胞功能指数(pancreatic β cell function index,HOMA-β)以及胰岛素抵抗指数(insulin resistance index,HOMA-IR)评价胰岛β细胞功能。HOMA-β=20×FINS(mIU/L)/[FBG(mmol/L)-3.5],HOMA-IR=FINS(mIU/L)×FBG(mmol/L)/22.5。④采用电阻抗法(欧姆龙DUALSCAN HDS2000)测量内脏脂肪面积(visceral fat area,VFA)和皮下脂肪面积(subcutaneous fat area,SFA)。由专门人员进行操作,其对患者分组情况毫不知情。计算VFA与SFA的比值(visceral to subcutaneous fat area ratio,VSR)。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS 19.0 统计学软件进行数据分析,计数资料以率表示,采用χ2检验;符合正态分布的计量资料以均数±标准差(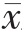 ±s)表示,两组间比较采用独立样本t检验,以P<0.05 为差异有统计学意义。
±s)表示,两组间比较采用独立样本t检验,以P<0.05 为差异有统计学意义。
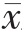 ±s)表示,两组间比较采用独立样本t检验,以P<0.05 为差异有统计学意义。
±s)表示,两组间比较采用独立样本t检验,以P<0.05 为差异有统计学意义。2 结果
2.1 两组患者不良反应及副作用的比较
两组患者治疗期间均未见严重呕吐、腹泻等不良反应以及严重低血糖事件,顺利完成治疗并纳入结果分析。
2.2 两组患者体重及血糖变化的比较
两组患者治疗前的体重、BMI、FBG、HbA1c比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);两组患者治疗后的体重、BMI、FBG、HbA1c均低于治疗前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。研究组患者治疗后的体重、BMI、FBG、HbA1c均低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表1)。
表1 两组患者治疗前后体重、BMI、FBG、HbA1c的比较(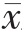 ±s)
±s)
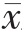 ±s)
±s).jpg)
2.3 两组患者胰岛β 功能、胰岛素抵抗以及体脂分布相关指标变化的比较
两组患者治疗前的HOMA-β、HOMA-IR比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);两组患者治疗后的HOMAβ 高于治疗前,HOMA-IR低于治疗前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);研究组患者治疗后的HOMA-β 高于对照组,HOMA-IR低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。两组患者治疗前的VFA、SFA、VSR比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);两组患者治疗后的VFA、SFA均低于治疗前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);研究组患者治疗后的VFA、SFA均低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);两组患者治疗前后VFA与SFA 的比值(VSR)比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)(表2)。
表2 两组患者治疗前后HOMA-β、HOMA-IR、VFA、SFA和VSR的比较(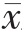 ±s)
±s)
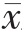 ±s)
±s).jpg)
3 讨论
肥胖会导致游离脂肪酸水平升高,脂肪可储存在非脂肪组织中,如肌肉、肝脏和胰腺等[3]。与皮下脂肪组织(subcutaneous adipose tissue,SAT)相比,VAT与T2DM患者动脉粥样硬化明显相关[6]。然而,除二甲双胍外,大多数降糖药物都会导致体重增加[7]。此外,糖尿病药物治疗是导致低血糖最常见的原因,患者可能会因此增加能量摄入而加剧体重增加[8]。既往关于利拉鲁肽对脂肪组织分布影响的研究结果不一,可能与研究对象基线特征、治疗方式、干预时间的长短和评估脂肪组织区域的方法存在差异有关[9-13]。LEAD-2和LEAD-3研究表明利拉鲁肽(单用或与二甲双胍联合使用)可持续改善血糖控制及减轻体重,且低血糖风险极低[9-10]。上述两研究利用双能X线吸收仪和CT 评估脂肪组织面积,结果显示利拉鲁肽对体重的减轻主要来自于脂肪量的减少。尽管VAT和SAT均有所减少,但VAT 的减少似乎更大。本研究也显示利拉鲁肽联合二甲双胍治疗后患者体重、BMI、VFA和SFA 低于单用二甲双胍的患者,但VSR 差异无统计学意义,与LEAD 2-3研究结果有所不同,可能与本研究样本量有关。利拉鲁肽对VAT 的影响可能与其减少巨噬细胞的浸润、直接抑制脂肪细胞和脂肪组织巨噬细胞的炎症途径有关,同时可能有助于改善胰岛素敏感性[14]。
随着病程进展,T2DM患者需要增加降糖药物[15],胰岛β细胞功能的逐步恶化是T2DM 的1个病理过程[16],目前还没有任何一种药物被证明能确切地防止T2DM患者β细胞功能下降[17]。因此,β细胞功能的保护仍然是T2DM 治疗中难以达到的目标。
本研究结果显示,利拉鲁肽联合二甲双胍较单用二甲双胍治疗患者血糖控制更理想,HOMA-β 升高及HOMA-IR 下降更明显,提示利拉鲁肽对胰岛功能有改善作用,与过往报道结果相似[9-10,12,18]。其中LIBRA 试验应用利拉鲁肽治疗48周,诱导了β细胞功能的进一步增强,然而,停药后2周内β细胞功能显著增强的现象完全丧失[18],提示β细胞功能的增加可能是由于体重减轻和(或)血糖水平降低引起,并不是利拉鲁肽的直接作用。因此,尽管利拉鲁肽使β细胞功能得到了改善,但并没有逆转β细胞恶化的潜在病理。
综上所述,利拉鲁肽可以降低超重/肥胖T2DM患者血糖、体重,改善脂肪分布、β细胞功能以及胰岛素抵抗,对延缓糖尿病进展有积极作用。
[参考文献]
[1]Zheng Y,Ley SH,Hu FB.Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications[J].Nat Rev Endocrinol,2018,14(2):88-98.
[2]Hansen E,Hajri T,Abumrad NN.Is all fat the same? The role of fat in the pathogenesis of the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Surgery,2006,139(6):711-716.
[3]Caspard H,Jabbour S,Hammar N,et al.Recent trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes and the association with abdominal obesity lead to growing health disparities in the USA:an analysis of the NHANES surveys from 1999 to 2014[J].Diabetes Obes Metab,2018,20(3):667-671.
[4]Drucker DJ,Nauck MA.The incretin system:glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes[J].Lancet,2006,368(9548):1696-1705.
[5]Agers H,Jensen LB,Elbrnd B,et al.The pharmacokinetics,pharmacodynamics,safety and tolerability of NN2211,a new long-acting GLP-1 derivative,in healthy men[J].Diabetologia,2002,45(2):195-202.
[6]Reijrink M,de Boer SA,Spoor DS,et al.Visceral adipose tissue volume is associated with premature atherosclerosis in early type 2 diabetes mellitus independent of traditional risk factors[J].Atherosclerosis,2019,290:87-93.
[7]Hermansen K,Mortensen LS.Bodyweight changes associated with antihyperglycaemic agents in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Drug Saf,2007,30(12):1127-1142.
[8]Russell-Jones D,Khan R.Insulin-associated weight gain in diabetes-causes,effects and coping strategies[J].Diabetes Obes Metab,2007,9(6):799-812
[9]Nauck M,Frid A,Hermansen K,et al.Efficacy and safety comparison of liraglutide,glimepiride,and placebo,all in combination with metformin,in type 2 diabetes:the LEAD(liraglutide effect and action in diabetes)-2 study[J].Diabetes Care,2009,32(1):84-90.
[10]Garber A,Henry R,Ratner R,et al.Liraglutide versus glimepiride monotherapy for type 2 diabetes (LEAD-3 Mono):a randomised,52-week,phase Ⅲ,double-blind,parallel-treatment trial[J].Lancet,2009,373(9662):473-481.
[11]Suzuki D,Toyoda M,Kimura M,et al.Effects of liraglutide,a human glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue,on body weight,body fat area and body fat-related markers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].Intern Med,2013,52(10):1029-1034.
[12]Santilli F,Simeone PG,Guagnano MT,et al.Effects of liraglutide on weight loss,fat distribution,and β-cell function in obese subjects with prediabetes or early type 2 diabetes[J].Diabetes Care,2017,40(11):1556-1564.
[13]Bizino MB,Jazet IM,de Heer P,et al.Placebo-controlled randomised trial with liraglutide on magnetic resonance endpoints in individuals with type 2 diabetes:a pre-specified secondary study on ectopic fat accumulation[J].Diabetologia,2020,63(1):65-74.
[14]Lee YS,Park MS,Choung JS,et al.Glucagon-like peptide-1 inhibits adipose tissue macrophage infiltration and inflammation in an obese mouse model of diabetes[J].Diabetologia,2012,55(9):2456-2468.
[15]Turner RC,Cull CA,Frighi V,et al.Glycemic control with diet,sulfonylurea,metformin,or insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus:progressive requirement for multiple therapies (UKPDS 49)[J].JAMA,1999,281(21):2005-2012.
[16]DeFronzo RA,Abdul-Ghani MA.Preservation of β-cell function:the key to diabetes prevention[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2011,96(8):2354-2366.
[17]Leahy JL,Hirsch IB,Peterson KA,et al.Targeting β-cell function early in the course of therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2010,95(9):4206-4216.
[18]Retnakaran R,Kramer CK,Choi H,et al.Liraglutide and the preservation of pancreatic β-cell function in early type 2 diabetes:the LIBRA trial[J].Diabetes Care,2014,37(12):3270-3278.
Influence of Liraglutide combined with Metformin on bodyweight, fat distribution and β-cell function in overweight/obese subjects with early type 2 diabetes mellitus
YE Jing-wen1 LIANG Wei-qiang1 SHU Yi1 DENG Jia-jin2▲
1.Department of Endocrinology, Affiliated Nanhai Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangdong Province, Foshan 528000, China;2.Department of Ophthalmology, Affiliated Nanhai Hospital of Southern Medical University,Guangdong Province, Foshan 528000, China.
1.Department of Endocrinology, Affiliated Nanhai Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangdong Province, Foshan 528000, China;2.Department of Ophthalmology, Affiliated Nanhai Hospital of Southern Medical University,Guangdong Province, Foshan 528000, China.
[Abstract]Objective To investigate the influence of Lilarutide combined with Metformin on bodyweight, fat distribution and β cell function in overweight/obese subjects with early type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).Methods A total of 80 newly diagnosed overweight/obese T2DM patients treated in our hospital from June 2018 to June 2019 were selected as the research objects, and they were divided into the study group and the control group by a random number table method, 40 cases in each group.The control group was treated with Metformin, and the study group was treated with Liraglutide on the basis of the control group.The treatment lasted 24 weeks.Changes in bodyweight, body mass index(BMI), fasting blood glucose (FBG), glycosylated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), visceral fat area (VFA), subcutaneous fat area (SFA), homeostasis model assessment-β cell (HOMA-β) and homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance(HOMA-IR) were compared between the two groups before and after treatment.Results After treatment, the bodyweight, BMI, FBG, HbA1c, HOMA-IR, VFA and SFA of the two groups were lower than those before treatment, and HOMA-β of the two groups was higher than that before treatment, with statistically significant differences (P<0.05).After treatment, the bodyweight, BMI, FBG, HbA1c, HOMA-IR, VFA and SFA of the patients in the study group were lower than those in the control group, and HOMA-β in the study group was higher than that in the control group, with statistically significant differences (P<0.05).There was no significant difference in the ratio of VFA to SFA (VSR) between the two groups before and after treatment (P>0.05).Conclusion Liraglutide has good effects on reducing glucose,weight loss, improving fat distribution and β cell function in overweight/obese subjects with early T2DM.
[Key words]Liraglutide;Type 2 diabetes mellitus;Bodyweight;Visceral adipose tissue;Islet beta cell
[中图分类号]R587.1
[文献标识码]A
[文章编号]1674-4721(2020)7(b)-0076-04
[作者简介]叶静文(1986-),女,硕士,主治医师,研究方向:内分泌疾病的诊治与研究
▲通讯作者
(收稿日期:2020-03-13)